
Boeing-Stearman Model 75
The Boeing-Stearman Model 75 was an American biplane formerly used as a military trainer aircraft by the U.S. Air Forces and U.S. Navy.
There are various types of aircraft, including airplanes, helicopters, gliders, airships, and hot air balloons. This page will allow you to quickly visit each type section more easily. Jump to:
Airplanes – Airships – Gliders – Helicopters – Hot Air Balloons
Airplanes have significantly impacted global connectivity, commerce, and tourism, shrinking distances and facilitating global transportation networks. They have revolutionized travel, enabled rapid delivery of goods, facilitated emergency response and medical evacuations, and played a crucial role in military operations and surveillance. Here is the access to the complete database (divided by Type):
Airplanes, also known as aeroplanes or fixed-wing aircraft, are the most common and widely used type of aircraft. They have fixed wings that generate lift as they move through the air. Airplanes can range from small single-engine aircraft used for recreational purposes to large commercial airliners and cargo planes capable of carrying hundreds of passengers or significant amounts of freight.

The Boeing-Stearman Model 75 was an American biplane formerly used as a military trainer aircraft by the U.S. Air Forces and U.S. Navy.

The Grumman F4F Wildcat is an American fighter aircraft used by the United States Navy and the British Royal Navy during WW2.

The Morane-Saulnier H was a French single-seat successful sporting and racing aircraft. It was the derivative of the Morane-Saulnier G.

The Lockheed Model 12 Electra Junior (or L-12) was an eight-seat, six-passenger all-metal twin-engine transport aircraft of the late 1930s.

The Voisin III was a French two-seater pusher biplane aircraft developed by Voisin in 1914 and used during World War I.
Helicopters are rotary-wing aircraft that use rotating blades on top to generate lift and propulsion. They have the unique ability to take off and land vertically and hover in one place. Helicopters are widely used in various applications, including transportation, search and rescue, and military operations.
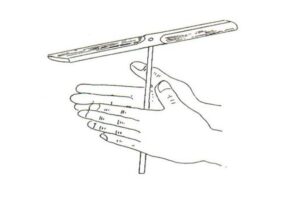
The Bamboo-Copter or Chinese Top is a toy helicopter rotor that flies up when its shaft is spun rapidly. The spinning creates lift.

Leonardo’s Aerial Screw was envisioned as a device resembling a large screw or corkscrew-shaped structure that would enable vertical flight.
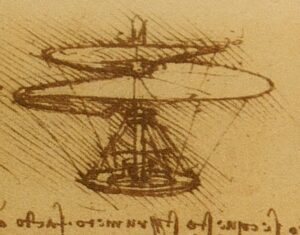
Leonardo’s Aerial Screw was envisioned as a device resembling a large screw or corkscrew-shaped structure that would enable vertical flight.

The Bell UH-1 Iroquois is a utility military helicopter and the first turbine-powered helicopter in service with the United States military.

The Boeing AH-64 Apache is an American twin-turboshaft attack helicopter primarily operated by the U.S. Army but used by many nations.
Gliders are unpowered aircraft that rely on the natural forces of wind and air currents to stay aloft. They have long wings and are designed to glide through the air for extended periods without an engine. Gliders are used for recreational flying, competitive soaring, and training purposes.

The General Aircraft Hamilcar (or Hamilcar Mark I) was a British military glider produced and used during the Second World War.

The DFS 230 was a German transport glider developed in 1933 and operated by the Luftwaffe during World War II.

The Bristol XLRQ was a 12-seat amphibious glider aircraft developed for the United States Marine Corps in 1942-43.

The Yokosuka Ro-go Ko-gata was a Japanese experimental glider used as a reconnaissance floatplane. It was developed during World War I.

The Airspeed AS.51 Horsa was a British troop-carrying glider developed and manufactured by Airspeed and used during the Second World War.
Airships, also known as dirigibles or blimps, are lighter-than-air aircraft that use large gas-filled envelopes for buoyancy. They have engines for propulsion and control surfaces for maneuverability. Airships are relatively slower than airplanes but offer unique capabilities for long-distance travel and aerial observation.

The Zeppelin LZ 10 Schwaben was a German rigid passenger airship built in 1911 by Luftschiffbau Zeppelin and operated by DELAG.

The SS Class Airship were cheap and simple small non-rigid airships or “blimps” designed to counter German U-boats.

His Majesty’s Airship R100, or R100, was a British rigid airship designed and constructed as part of an ambitious experiment in the 1920s.

The De Gusmao Steam Airship was a picture and description of an airship made by Bartolomeu Lourenço de Gusmão to King João V in 1709.

Lana de Terzi’s Flying Boat was an early experimental aircraft built by Enrico Forlanini and Giovanni Battista “Lana” de Terzi in 1905.
Hot air balloons are aircraft that use hot air to generate lift. They consist of a large envelope filled with heated air and are propelled by wind currents. Hot air balloons are primarily used for recreational purposes and provide a serene and scenic flying experience.

The Breitling Orbiter 3 was a historic hot air balloon that achieved the first successful nonstop circumnavigation of the globe in 1999.

The Virgin Atlantic Flyer was a groundbreaking hot air balloon piloted by entrepreneur Richard Branson and Swedish aeronaut Per Lindstrand.

The Double Eagle II was the first balloon to cross the Atlantic Ocean. It left Maine and landed on 17 August 1978 near Paris.

The Spirit of Freedom was a groundbreaking hot air balloon that marked a historic achievement in aviation. Learn more about it.

This successful demonstration of hydrogen as a lifting gas paved the way for subsequent manned flights and further developments.