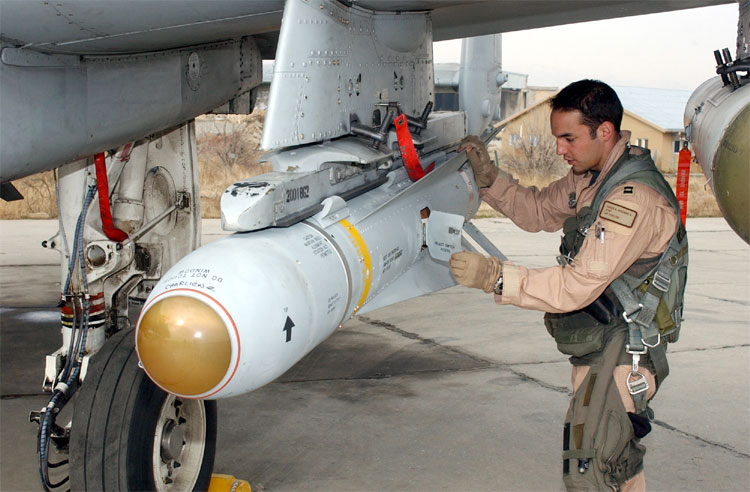
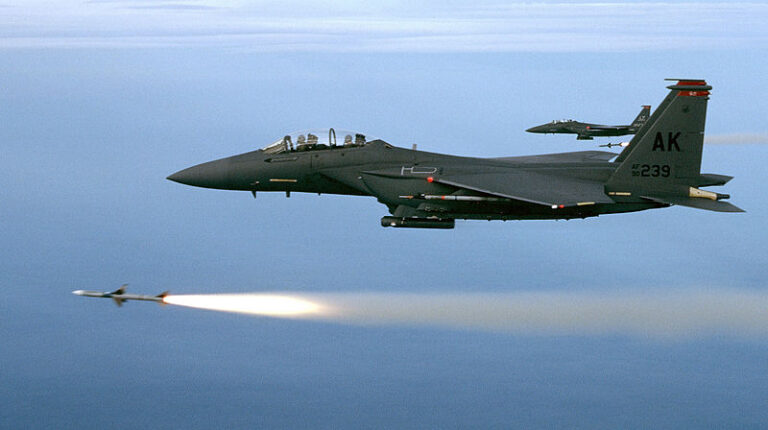
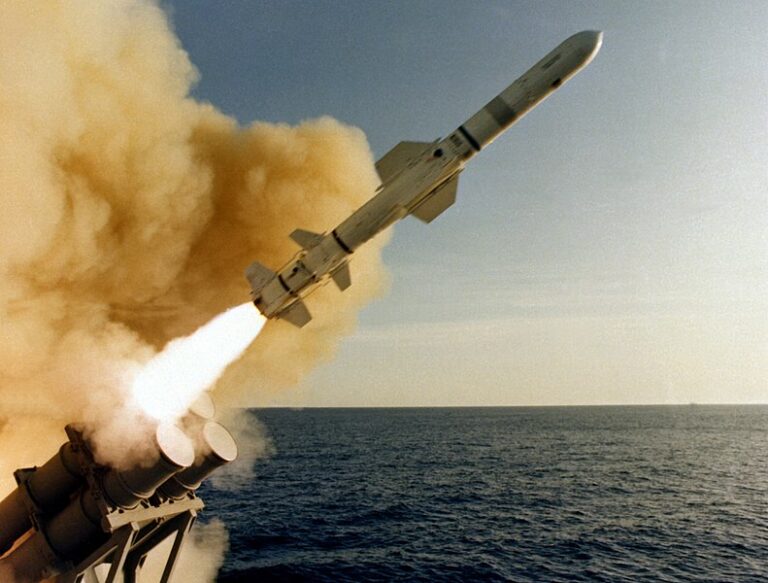
At the core of the formidable might of military aviation lies an impressive arsenal of weapons systems, meticulously designed to unleash devastation upon adversaries or precisely engage targets with surgical precision. From air-to-air missiles capable of reaching supersonic speeds to precision-guided bombs capable of hitting targets with unmatched accuracy, aircraft weapons systems embody the cutting edge of military technology.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of aircraft weapons systems, uncovering the breadth and capabilities of these lethal tools that adorn the wings and fuselages of modern warplanes. By understanding the complexities and advancements in this field, you will be able to gain a deeper appreciation for the role these systems play in shaping the outcomes of aerial warfare.
Exploring the Diverse Array of Aircraft Weapons Systems
It is through the intricacies of aircraft weapons systems that cutting-edge technology converges with military strategy to shape the battlefield and redefine the very nature of modern warfare. So, what are the main components of aircraft and warplanes weapons systems?
First, we will explore the key components of aircraft weapons systems, their purpose, and the strategies employed in employing them effectively. Then, we will uncover the evolving technologies that have revolutionized the face of aerial combat, from long-range standoff weapons to precision-guided munitions guided by advanced target acquisition systems. So, let’s get started, shall we?
Aircraft Weapons: Missiles
When it comes to aerial warfare, the role of missiles cannot be overstated. These advanced projectiles, carefully designed and equipped with cutting-edge technology, are the cornerstone of modern aircraft weapons systems.
From engaging airborne adversaries to striking ground-based targets and even combating naval threats, aircraft missiles exemplify the relentless pursuit of precision and destructive power in the skies.
Air-To-Air Missiles (AAMs)
These weapons are designed to engage and destroy enemy aircraft. Air-to-Air Missiles, or AAMs, feature sophisticated guidance systems, such as radar, infrared, or active/passive homing, enabling them to track and intercept airborne targets with remarkable accuracy. Typically, MMAs are equipped with propulsion systems to achieve high speeds and maneuverability.
Some examples of AAMs include:
AIM-9 Sidewinder: A widely used short-range air-to-air missile known for its infrared homing capability, allowing it to track and engage enemy aircraft using heat signatures. For example, the F-15 Eagle, F-16 Fighting Falcon, and F-22 Raptor have all employed AIM-9 missiles.
AIM-120 AMRAAM: A medium to long-range air-to-air missile with active radar guidance, providing high accuracy and effectiveness against a wide range of targets.
R-77 (AA-12 Adder): A Russian beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile featuring an active radar seeker and impressive maneuverability, designed to engage targets at extended distances.
Meteor: A European advanced long-range air-to-air missile equipped with active radar guidance and a ramjet engine, offering exceptional range and high-end maneuverability. Some notable aircraft that are equipped with Meteor missiles include the Eurofighter Typhoon, Dassault Rafale, and Saab JAS 39 Grippen.
PL-15: A Chinese beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile known for its long-range capabilities, active radar seeker, and advanced electronic counter-countermeasures to overcome enemy defenses.
Air-to-Ground Missiles (AGMs)
Air-to-Ground Missiles (also known as AGMs or Air-to-Surface missiles) are utilized to strike ground-based targets, such as enemy vehicles, structures, or installations. They employ a variety of guidance systems, including laser, radar, or GPS, to ensure precision strikes. AGMs often have different warhead options, including high-explosive, armor-piercing, or cluster munitions, to suit various mission requirements.
Some examples of AGMs include:
AGM-65 Maverick: A widely deployed air-to-ground missile used by various military aircraft. It utilizes electro-optical, infrared, or laser guidance systems and is effective against a range of ground targets, including armored vehicles and structures.
Brimstone: A precision air-to-ground missile developed in the United Kingdom, renowned for its accuracy and versatility. It employs radar and laser guidance systems, making it effective against armored vehicles and fast-moving targets. The Brimstone missile is primarily used by the Eurofighter Typhoon, Panavia Tornado GR4, and General Atomics MQ-9 Reaper.
AGM-158 JASSM: A stealthy long-range air-to-ground missile that can be launched from a significant distance. It utilizes inertial navigation and GPS for guidance, enabling it to strike high-value targets with remarkable accuracy.
Kh-29: A Russian air-to-ground missile used for anti-ship and land attack missions. It employs laser guidance and can carry a variety of warheads, including high-explosive and armor-piercing, to engage different types of targets.
Spike NLOS: A versatile air-to-ground missile developed in Israel, featuring long-range capabilities and multi-mode guidance systems, including electro-optical and infrared. It is suitable for engaging both stationary and moving targets, including armored vehicles and fortified structures.
Anti-Ship Missiles (AShMs)
These specialized missiles are designed specifically for engaging naval vessels. Anti-ship missiles (or AShMs) possess the capability to track and engage moving targets over long distances and are equipped with features like sea-skimming abilities and advanced target discrimination capabilities.
Some examples of AShMs include:
Harpoon: Widely used anti-ship missile with over-the-horizon capabilities, utilized by numerous navies worldwide.
Exocet: A renowned French-built anti-ship missile, known for its sea-skimming capabilities and deadly effectiveness against naval targets.
BrahMos: A joint Indian-Russian supersonic anti-ship missile, capable of striking targets at high speeds with precision and devastating impact.
NSM (Naval Strike Missile): A modern anti-ship missile with advanced target recognition and sea-skimming capabilities, providing superior lethality against enemy vessels.
C-802: A Chinese anti-ship missile, designed to engage and neutralize naval targets with its radar-guided and sea-skimming capabilities.
Aircraft Weapons: Bombs
Aicraft bombs are formidable weapons, carefully engineered and designed to deliver devastation from the skies. Bombs typically play a pivotal role in shaping the outcome of military operations.
Guided Bombs
Also known as precision-guided munitions (PGMs), these bombs have integrated guidance systems that enable them to achieve high accuracy when engaging ground targets. They can be guided using laser, GPS, or inertial navigation systems, and some even feature target-seeking capabilities for real-time adjustments during flight.
Some examples of guided bombs include:
JDAM (Joint Direct Attack Munition): A widely used guided bomb that converts conventional “dumb” bombs into precision-guided munitions by adding a GPS guidance kit.
Paveway: A family of laser-guided bombs offering increased accuracy and target engagement capabilities for various aircraft platforms.
SDB (Small Diameter Bomb): A compact guided bomb designed for high precision and reduced collateral damage, equipped with GPS and inertial navigation system guidance.
KAB-500: A Russian guided bomb featuring a range of warheads and guidance options, including laser, infrared, and satellite-based navigation systems.
GBU-39/B (Brimstone): A guided bomb utilized by several nations, known for its small size, high accuracy, and versatile engagement capabilities against a wide range of ground targets.
Cluster Bombs
Cluster bombs disperse a large number of smaller bomblets over a wide area. These bomblets are designed to explode on impact, effectively engaging multiple targets simultaneously. Cluster bombs are typically used against enemy formations or when area saturation is desired.
Some examples of cluster bombs used by aircraft include:
CBU-97 Sensor Fuzed Weapon: A cluster bomb that dispenses submunition, which uses infrared and laser sensors to detect and engage armored vehicles.
RBK-500 Cluster Bomb: A Russian-designed cluster bomb that disperses bomblets over a wide area to target enemy personnel and vehicles. Many Sukhoi and Mikoyan aircraft used RBK-500s.
BLU-108/B SFW (Smart Submunition): A cluster bomb that deploys submunitions equipped with infrared sensors to detect and engage armored targets.
M26 Cluster Bomb: An American-made cluster bomb that releases submunition to cover a large area, targeting enemy vehicles and personnel.
KMGU-2: A Russian cluster bomb dispenser capable of releasing a variety of submunitions, including anti-tank and anti-personnel bomblets, to engage multiple targets simultaneously.
Anti-Runway Penetration Bombs
Anti-runway bombs are specifically designed to disable or destroy enemy runways, rendering them unusable for aircraft operations. They often feature specialized warhead designs, such as penetrator or earth-penetrating munitions, to inflict significant damage to the runway surface or underlying infrastructure.
Some examples of anti-runway penetration bombs include:
BLU-113 Penetrator: A bunker-busting bomb designed to penetrate hardened structures, including runways, with its specialized warhead.
GBU-28/B Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP): A large, precision-guided bomb developed to penetrate deeply buried targets, such as runways and underground facilities.
Durandal: A French-designed anti-runway bomb, designed to penetrate the surface of the runway and create craters, rendering it temporarily or permanently unusable.
BLU-116/B Anti-Runway Bomb: A bomb specifically designed for runway denial, featuring a warhead optimized for disrupting and disabling enemy airfields.
Popeye Turbo: An air-launched cruise missile equipped with a penetrating warhead, capable of engaging and neutralizing hardened runways and other critical infrastructure.
Other Aircraft Weapons
In addition to missiles and bombs, aircraft weapons systems consist of supporting components, such as launch systems, guidance control units, and targeting sensors. These systems work in tandem to ensure accurate deployment and maximize mission effectiveness.
It’s worth noting that modern aircraft weapons systems increasingly integrate advanced technologies, such as network-centric warfare capabilities, data link communication, and real-time target updates. These advancements enable seamless coordination with other friendly forces and enhance the overall situational awareness and effectiveness of the weapon systems.
Aircraft Weapon Systems: The Future
As warfare evolves, continuous research and development efforts focus on improving the performance, range, speed, and precision of these weapons, allowing warplanes to maintain their dominance in the ever-changing landscape of aerial combat.